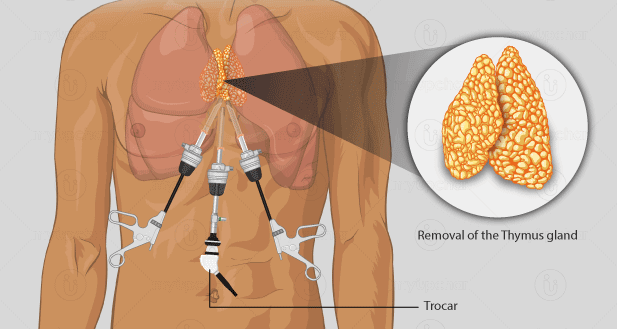
Thymectomy
India
-
Our Price USD 3060
-
Hospital Price USD 3400
-
You Save : USD 340
Booking Amount: USD 306. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Thymectomy:
It is a surgical operation in which thymic tissue is removed from the thymus. To assure the removal of all accessible thymus, a "maximal" thymectomy is necessary. All patients receiving thymectomy for myasthenia gravis with or without thymoma and in the treatment of myasthenia gravis with or without myasthenia gravis should have this surgery done.
Thymus is a gland located in the chest that aids in the development of the body's immune system. A thymectomy, on the other hand, is a surgical treatment that removes the thymus gland. It is no longer used to treat Myasthenia Gravis in the hopes of boosting the disease's chances of remission.
Disease Overview:
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular condition caused by an autoimmune disease that produces weakening in the skeletal muscles that increases with exercise and improves with rest. These muscles are in charge of breathing and moving various portions of the body, such as the arms and legs.
Disease Signs and Symptoms
Muscle weakness that increases after times of exertion and improves after periods of rest is a characteristic of myasthenia gravis. The condition frequently (but not always) involves muscles that govern eye and eyelid movement, facial expression, chewing, talking, and swallowing.
The development of the condition can be rapid, and the symptoms of myasthenia gravis are frequently misdiagnosed. Myasthenia gravis causes varying degrees of muscular weakening in different people.
Myasthenia gravis patients may have the following symptoms:
- Muscle weakness in the eyes (called ocular myasthenia)
- one or both eyelids dropping (ptosis)
- double vision or muddled vision (diplopia)
- a change in facial expression swallowing difficulties shortness of breath poor speaking (dysarthria)
- Arms, hands, fingers, legs, and neck weakness.
- Myasthenia gravis causes extreme weakness that can lead to respiratory failure, which need prompt medical attention.
Disease Causes:
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune illness, which means the immune system fights itself instead of protecting the body from outside invaders.
Myasthenia gravis is caused by a malfunction in nerve impulse transmission to muscles. It happens when neuron and muscle communication is disrupted at the neuromuscular junction, which is where nerve cells join to the muscles they regulate.
Neurotransmitters are molecules that transfer information between neurons, or brain cells. When electrical signals or impulses travel along a motor neuron, the nerve terminals normally produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that binds to acetylcholine receptors on the muscle. When acetylcholine binds to its receptor, it stimulates the muscle and causes it to contract.
Antibodies (immune proteins generated by the body's immune system) block, modify, or kill acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis, preventing the muscle from contracting. Antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor are the most common cause, although antibodies to other proteins, such as MuSK (Muscle-Specific Kinase), can also disrupt transmission at the neuromuscular junction.
The thymus gland is a gland found in the chest.
Myasthenia gravis is linked to the thymus gland, which regulates immunological function. It develops slowly until adolescence, after which it shrinks and is replaced by fat.
The thymus is responsible for creating T-lymphocytes or T cells, a kind of white blood cell that defends the body from viruses and illnesses, and it plays a vital part in the development of the immune system throughout childhood.
Disease Diagnosis:
To confirm the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis, a doctor may perform or request numerous tests:
A physical and neurological examination will be performed. A physician will initially do a physical examination and assess the patient's medical history. The physician will assess muscular strength and tone, coordination, sense of touch, and look for eye movement impairment during a neurological examination.
A test for edrophonium. This test employs edrophonium chloride injections to temporarily alleviate weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. The medication prevents acetylcholine breakdown and momentarily raises acetylcholine levels at the neuromuscular junction. It's most commonly used to check for ocular muscle weakness.
A blood test is required. Antibodies against acetylcholine receptors are unusually high in most people with myasthenia gravis. In around half of people with myasthenia gravis who don't have acetylcholine receptor antibodies, a second antibody termed anti-MuSK antibody has been discovered. This antibody can also be detected by a blood test. However, neither of these antibodies are present in some people with myasthenia gravis. These people are believed to have seronegative (antibody-free) myasthenia
Electrodiagnostics. Repetitive nerve stimulation is a diagnostic technique that involves repeatedly stimulating a person's nerves with tiny electrical pulses to weary certain muscles. Myasthenia gravis muscle fibres, like those in other neuromuscular illnesses, do not react as effectively to repeated electrical stimulation as those in healthy people. The most sensitive diagnostic for myasthenia gravis is single fibre electromyography (EMG), which identifies decreased nerve-to-muscle communication. When other tests fail to show abnormalities, EMG can be extremely helpful in detecting mild instances of myasthenia gravis.
Imaging for diagnostic purposes. A thymoma can be detected via diagnostic imaging of the chest, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Pulmonary function tests are used to determine how well your lungs are working. Measuring breathing strength can aid in predicting whether or not respiration will fail, resulting in a myasthenic crisis.
Because weakness is a sign of many different diseases, the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is frequently overlooked or delayed (sometimes up to two years) in persons who have modest weakness or weakness that is limited to a few muscles.
Disease Treatment:
Myasthenia gravis can now be managed in most cases. There are a variety of treatments available to aid with muscular weakness reduction and improvement.
Thymectomy. By normalising the immune system, this procedure to remove the thymus gland (which is typically aberrant in persons with myasthenia gravis) can lessen symptoms and even cure some people. Thymectomy is beneficial for both persons with thymoma and those who have no evidence of the tumours, according to a NINDS-funded research. The operation decreased muscular weakness and the need for immunosuppressive medicines in 126 persons with myasthenia gravis and no visible thymoma, according to the clinical trial.
Antibody that is monoclonal. This medication aims to stop cholinergic antibodies from causing damage to the neuromuscular junction. Eculizumab was licenced by the United States Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for the treatment of generalised myasthenia gravis in people who test positive for the antiacetylcholine receptor (AchR) antibody.
Anticholinesterase medicines are drugs that inhibit the enzyme cholinesterase. Anticholinesterase medications such as mestinon or pyridostigmine, which decrease the breakdown of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction and hence enhance neuromuscular transmission and muscle strength, are used to treat the disease.
Drugs that inhibit the immune system. By inhibiting the formation of aberrant antibodies, these medicines boost muscular strength. Prednisone, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and tacrolimus are among them. The medications can have serious negative effects and need to be closely monitored by a doctor.
Intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis In severe instances of myasthenia gravis, these treatments may be a possibility. Antibodies attacking the neuromuscular junction can be found in plasma (a liquid component of blood). These therapies work by removing the harmful antibodies, but their effects generally only last a few weeks to months.
Plasmapheresis is a method in which dangerous antibodies in plasma are removed and replaced with good plasma or a plasma replacement using a machine.
Intravenous immunoglobulin is a highly concentrated infusion of antibodies derived from a large number of healthy donors that alters the immune system's function temporarily. It works by attracting and eliminating the antibodies that cause myasthenia gravis from circulation.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
7 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Umesh Kohli
Interventional Cardiologist- Echocardiography, Pacemaker Implantation, Coronary Angiography, Coronary Angiogram, Cardiac Ablation, Cardiac Catheterisation, ASD VSD repair, Cardioversion, Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDS), Peripheral Angioplasty, Non Invasive Cardiology, Chest Pain Treatment, Bypass Surgery, CT angiogram, Cardiology, Balloon Mitral Valbuloplasty
Accord Super specialty Hospital Faridabad, India
24 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Sumit Narang
Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgeon- Heart Failure Treatment, LVAD, Tricuspid, CABG on beating heart, Aortic Aneurysm Surgery, Double Valve Replacement, MVR, AVR, Peripheral & Carotid angioplasty and Stenting, TAVI/TAVR, PDA & ASD closures, VSD, Adult Valvuloplasty (mitral etc.)
Marengo Asia hospital, Faridabad Faridabad, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Vineet Bhatia
Cardiologist- Pacemaker Implantation, Coronary Angiography, Coronary Angioplasty / Bypass Surgery, Cardiac Catheterisation, Pacemaker Implantation, Balloon Valvuloplasty, AICD Implantation, EPS, Optical Coherence Tomography, RFA, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Catheterisation, Pacemaker Implantation, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Catheterisation
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
23 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Rajiv Parakh
Vascular surgeon- Carotid Surgery, Endovascular Interventions
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
35 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Adarsh Koppula
Cardiac Surgeon- CABG on beating heart, CABG on beating heart, Valve replacement / repair, Blood Conversation in Cardiac Surgery
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
37 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rajnees Malhotra
Cardiac Surgeon- Left ventricular assist device (LVAD), Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, Heart transplant, Heart Failure Treatment, Minimally invasive Cardiac Surgery, Heart transplant, Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation-ECMO, Robotic Cardiac Surgery, Mitral Valve Replacement & Repairs, Atrial Septal Defects (ASDS), Aortic Valve Replacement & Repairs
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Kumud Rai
Vascular surgeon- Aortic Aneurysm Surgery, Congenital Heart Disorder CHD, Correction of Varicose Veins, Aneurysmectomy and Peripheral Bypass Surgery
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
29 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. S. Radha Krishnan
Interventional Cardiologist- Pacemaker Implantation, Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), Coronary Angiography, Cardiac Ablation, Cardiac Catheterisation, Aortic Anuerysm Surgery/ Endovascular Repair, Cardioversion, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDS), Pacemaker Implantation, Peripheral Angioplasty, PCI, TMT, TOF, PDA, DGTA, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Catheterisation, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Pacemaker Implantation, Peripheral Angioplasty, Cardiac Ablation, Cardioversion, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Catheterisation
Fortis Escorts Heart Institute New Delhi, India
40 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Roopa Salwan
Cardiologist- Echocardiography, Left ventricular assist device (LVAD), Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, Pacemaker Implantation, Coronary Angiography, Bypass Heart Surgeon, Epilepsy Disorder, Cerebral Palsy Surgeon, Balloon Angioplasty, Mitral valve replacement, Cardiac Ablation, Congenital Heart Disorder CHD, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Pacemaker Implantation, Hypertension Treatment, ICD implantation, Mycardial Infarction, Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At, Holistic Heart Wellness & Health Care - Ayurveda, Preventing Post Bypass Surgery Blockages, Preventing Restenosis, Stent Surgery, PTCA or Coronary Angioplasty, Myocarditis Treatment, Atrial fibrillation treatment, Mitral insufficiency treatment, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment, Ventricular tachycardia treatment, Cardiac catheterizations, Hip Disorders, Pacemaker Implantation, Echocardiography, Hypertension Treatment, Echocardiography, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Ablation, Pacemaker Implantation
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
32 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Kumud rai
Vascular surgeon- Aortic Aneurysm Surgery, Congenital Heart Disorder CHD, Correction of Varicose Veins, Aneurysmectomy and Peripheral Bypass Surgery
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
29 Years of Experience