PA Banding
India
-
Our Price USD 3420
-
Hospital Price USD 3800
-
You Save : USD 380
Booking Amount: USD 342. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
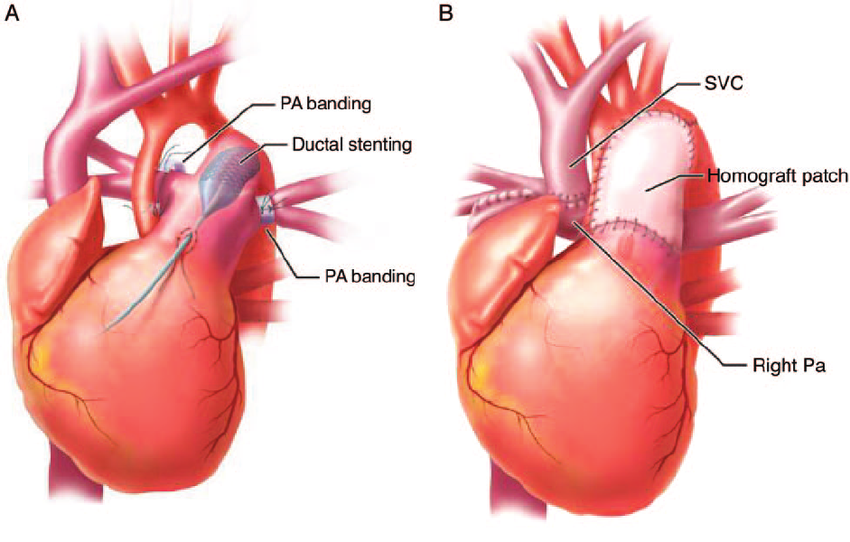
PA Banding:
Pulmonary artery banding (PAB) is a palliative surgical procedure used to treat congenital heart abnormalities defined by pulmonary overcirculation caused by blood shunting from left to right. PAB is only used to relieve pain in a certain group of infants with complicated congenital heart disease.
Disease Overview:
Congenital cardiac defects
Your kid was born with a problem in the structure of his or her heart if he or she has a congenital heart defect.
Some children's congenital cardiac abnormalities are minor and do not require therapy. Other congenital cardiac problems in children are more complicated and may need many procedures over several years.
Understanding your child's congenital heart problem will help you comprehend the situation and what to expect in the months and years ahead.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Congenital cardiac abnormalities that are serious are generally discovered immediately after birth or within the first few months of life. The following are possible signs and symptoms:
- Skin that is pale grey or blue in hue (cyanosis)
- Breathing quickly
- Swelling in the legs, belly button, or eyelids
- Shortness of breath during meals, resulting in inadequate weight gain
Congenital cardiac abnormalities that are less significant may not be detected until later in infancy. In older children, signs and symptoms of congenital cardiac abnormalities may include:
- Getting out of breath easily during exercise or activity
- Easily exhausted through physical exertion or exercise
- Experiencing dizziness or fainting during physical activity
- Hands, ankles, and feet swelling
Disease Causes:
The majority of congenital heart abnormalities are caused by issues that arise during the development of the baby's heart before birth. Most congenital cardiac abnormalities have an unknown origin. Certain environmental and genetic risk factors, on the other hand, may have a role. They are as follows:
Rubella is a contagious disease that affect (German measles). Rubella can affect your baby's heart development if you get it while pregnant. Before you are pregnant, your doctor can check for immunity to this viral illness and vaccine you if you aren't.
Diabetes. By carefully regulating blood sugar levels before and during pregnancy, a woman who had diabetes before becoming pregnant can lower her risk of congenital heart abnormalities. Diabetes that develops during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) does not raise the chance of a heart abnormality in the newborn.
Medications. Certain drugs can cause birth problems, including congenital heart disorders, if used during pregnancy. Before attempting to conceive, give your doctor a thorough list of your drugs.
Thalidomide (Thalomid), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, statins, the acne treatment isotretinoin (Absorica, Amnesteem, others), several epileptic medications, and some anxiety drugs are all known to raise the risk of congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Consumption of alcoholic beverages when pregnant. Consumption of alcoholic beverages during pregnancy raises the chance of congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Smoking. Quit smoking if you're a smoker. Smoking during pregnancy raises the likelihood of the baby developing a congenital heart condition.
Genetics and family history Congenital cardiac problems can run in families (i.e., they are inherited) and be linked to a genetic condition. Heart abnormalities are common in children who have an additional 21st chromosome (Down syndrome). Heart abnormalities can potentially be caused by a missing piece of genetic material (deletion) on chromosome 22.
Disease Diagnosis:
While the kid is still in the pregnancy, several congenital cardiac problems can be detected. A foetal ultrasound, a normal prenatal test used to monitor a baby's growth and development throughout pregnancy, can reveal signs of some cardiac problems.
If your kid seems blue, has abnormal growth, or your child's doctor hears an abnormal heart sound (murmur) while listening to your child's heart with a stethoscope after delivery, your child may have a congenital heart condition.
The majority of heart murmurs are benign, which means there is no heart defect present and the murmur is not harmful to your child's health. However, irregular blood flow to and from the heart can generate certain murmurs.
Tests
The following tests can be used to identify a congenital cardiac defect:
Pulse oximetry is the measurement of oxygen saturation in the blood. This simple, noninvasive test determines how much oxygen is present in your child's blood. The amount of oxygen in your child's blood is measured by a sensor attached to his or her fingertip. A lack of oxygen might indicate that your child has a heart or lung condition.
An EKG is a type of electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This noninvasive test monitors your child's heart's electrical activity. It can aid in the diagnosis of cardiac abnormalities or irregular heartbeats. On your baby's chest, sticky patches containing sensors (electrodes) are applied. The patches are connected to a computer through wires, which shows the results.
Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram creates pictures of your or your child's heart in action using sound waves (ultrasound). The cardiac valves and heart muscle can be seen during an echocardiogram. A foetal echocardiography is an echocardiogram performed on a baby before birth.
X-ray of the chest. A chest X-ray may be performed on your kid to see if the heart is enlarged or if the lungs contain excess blood or other fluid. These symptoms might indicate cardiac failure.
Catheterization of the heart. A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is placed into a blood artery in the groyne area and directed to the heart during this examination. Catheterization can provide more specific information on heart function and blood flow to your child's doctor. During cardiac catheterization, several heart therapies are possible.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the heart (MRI). The use of a cardiac MRI to diagnose and assess congenital heart abnormalities in adolescents and adults is becoming more widespread. A heart MRI provides three-dimensional images of the heart, allowing for precise measuring of the chambers.
Disease Treatemnt:
Treatment for congenital heart problems in children is determined by the kind of heart defect and its severity. A congenital cardiac abnormality may have no long-term consequences for your child's health and can thus be left untreated. Small holes, for example, may seal as your child grows older.
Serious cardiac problems must be treated as soon as possible when they are discovered. Medication, cardiac surgeries, or a heart transplant may be used to treat the condition.
Medications
Medications can be used alone or in combination with a cardiac treatment to treat symptoms or consequences of a congenital heart problem. The following medications are used to treat congenital cardiac defects:
Medications that help with heart rhythm. Anti-arrhythmic drugs assist to manage an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
Surgical or non-surgical techniques
A cardiac treatment or surgery may be needed if your kid has a serious congenital heart problem. The following techniques and surgeries are used to address congenital cardiac defects:
Cardiac intervention in the foetus If a significant flaw is discovered before birth, there is a chance that a surgery can be performed during pregnancy to fix the condition or assist lessen the defect's complications as the child develops. Fetal cardiac intervention is a rare occurrence that occurs only in extremely limited conditions.
Catheterization of the heart. Congenital heart abnormalities are treated in some children and adults using thin, flexible tubes (catheters). Without open-heart surgery, cardiac catheterization can be performed to repair holes in the heart or narrowing regions.
A doctor inserts one or more catheters into a blood artery, usually in the groyne, and into the heart during cardiac catheterization. To fix the defect, tiny instruments are passed via the catheter to the heart. Some catheter operations must be performed in stages over several years.
Surgery on the heart is performed. To correct a congenital heart abnormality, your kid may require open-heart surgery or minimally invasive heart surgery.
A heart transplant is a procedure in which a person' A heart transplant may be required if a major cardiac defect cannot be fixed.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
6 Days
Days in Hotel
*
12 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Krishan Chugh
Pediatrician- Pediatric Pulmonology, Allergy Specialist, Bronchoscopy, Bronchoscopy, Bronchoscopy, Pediatric Neonatalogy, Bronchoscopy, Bronchoscopy
Fortis Memorial Research Institute Gurgaon, India
39 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Bipin Kumar Dubey
Cardiologist- Angioplasty, ICD implantation, Coronary interventions, Balloon aortic valvotomy, Balloon pulmonary valvotomy, Paediatric cardiology, Baloon mitral valvotomy, Angioplasty, Balloon Mitral Valbuloplasty
Manipal Hospitals New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Krishna yadav
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatrics, General Surgery, General Surgery, General Surgery
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
56 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Brahmadeva Dwivedi
Pediatric surgeon- Bariatric Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Vascular Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Bariatric Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Vascular Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, General Surgery, General Surgery, General Surgery, Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgery, Pediatric Kidney Diseases, Pediatric Cancer Surgery, Pediatric Liver Transplant, Pediatric Lung Transplant, Pediatric Gastric Internal Surgery
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
63 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Meera Luthra
Pediatric surgeon- Laparoscopic and Miniamally Invasive Surgery, Newborn and Thoracoscopy
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
38 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rakesh Handa
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgeon, Neonatal Surgeon, Hypospadias Surgery, Surgery for Spinal Dysraphism
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
38 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Anurag Krishna
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgeon, Neonatal Surgeon, Endourology, Kidney obstructions, VU reflux, Complex birth defects, Hypospadias Surgery, Endourology
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
35 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Nasir Munim
Pediatrician- Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, Allergy Testing, Infant & Child nutrition, Allergy Testing, Atrial Septal Defects (ASDS), Thyroid disorder, Vaccination/ Immunization, Chickenpox Treatment, Asthma, Jaundice Treatment, Asthma, Cerebral Palsy, Vaccination/ Immunization, Infant & Child nutrition, Chickenpox Treatment, Chickenpox Treatment, Allergy Testing, Infant & Child nutrition, Bedwetting treatment and management, Polio, Infant & Child nutrition, Child Care, Lactation problems, Management of Restless Child Disorder, Child and Adolescent Problems, Chickenpox Treatment, Cerebral Palsy, Neurofibromatosis, Treatment of Sids, Cough in Children, Management of Growth Retardation, Multiple System Atrophy, Jaundice Treatment, Child and Adolescent Problems, Asthma, Allergy Testing
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
20 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Gaurav Kumar
Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon- Arterial switch operation, Double switch operation, Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, Arch repair, ASD VSD repair, Tetralogy of Fallot repair, Truncus arteriosus repair, Rastelli operation & Cone repair and cardiac transplant
Narayana Super Speciality hospitals Gurgaon, India
21 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Anil Bhan
Cardiac Surgeon- Pediatric Cardiology, Pediatric Cardiac Surgeon
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
37 Years of Experience