Diagnostic Lap
India
-
Our Price USD 1350
-
Hospital Price USD 1500
-
You Save : USD 150
Booking Amount: USD 135. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Diagnostic Lap
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a procedure that allows a clinician to examine the contents of the abdomen or pelvis up close and personal.
Disease Overview:
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a painful condition in which tissue that looks like the endometrium that typically lines the inside of your uterus grows outside of it. Endometriosis affects your ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the tissue lining your pelvic most often. Endometrial-like tissue can occasionally be detected outside of the pelvic organs' region.
With endometriosis, the endometrial-like tissue swells, breaks down, and bleeds with each menstrual cycle, much like endometrial tissue would. However, because this tissue can't leave your body, it becomes imprisoned. Endometriomas are cysts that occur when endometriosis affects the ovaries. Surrounding tissue can become inflamed, leading to the formation of scar tissue and adhesions – fibrous bands that can cause pelvic tissues and organs to cling together.Endometriosis can cause considerable discomfort, particularly during menstrual cycles. Fertility issues may also arise. Effective therapies are, fortunately, accessible.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Pelvic discomfort is the most common symptom of endometriosis, which is commonly coupled with menstrual cycles. Although many women feel cramps during their periods, individuals who have endometriosis report discomfort that is significantly severe than usual. Pain may also worsen with time.
Endometriosis is characterised by the following signs and symptoms:
- Periods of suffering (dysmenorrhea). Pelvic discomfort and cramps can start before a menstrual cycle and last for many days. You may also have discomfort in your lower back and abdomen.
- Intercourse causes pain. Endometriosis can cause pain during or after intercourse.
- Pain during urinating or bowel motions. These symptoms are most likely to occur during a menstrual cycle.
- Bleeding that is excessive. You may have heavy menstrual cycles or bleeding between periods on occasion (intermenstrual bleeding).
- Infertility. Endometriosis is sometimes discovered when seeking therapy for infertility.
- Other indications and symptoms may be present. During menstrual cycles, you may have tiredness, diarrhoea, constipation, bloating, or nausea.
Your pain level may not be an accurate predictor of the severity of your ailment. You might have moderate endometriosis with a lot of discomfort or advanced endometriosis with very little pain.
Disease Causes
Although the specific aetiology of endometriosis is unknown, the following are some plausible explanations:
Menstruation in reverse. Menstrual blood including endometrial cells travels back through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvic cavity instead of out of the body during retrograde menstruation. These endometrial cells adhere to the pelvic walls and the surfaces of pelvic organs, where they proliferate, thicken, and bleed during each menstrual cycle.
Peritoneal cells undergo transformation. Experts argue that hormones or immunological factors stimulate the transition of peritoneal cells — cells that line the inner wall of your belly — into endometrial-like cells, which is known as the "induction theory."
Transformation of embryonic cells. During puberty, hormones like oestrogen can change embryonic cells (cells in the early stages of development) into endometrial-like cell implants.
Scar implantation by surgery. Endometrial cells may cling to a surgical incision after a procedure such as a hysterectomy or C-section.
Transport of endometrial cells. Endometrial cells may be transported to different areas of the body via blood vessels or the tissue fluid (lymphatic) system.
Disorder of the immune system. The body may be unable to identify and kill endometrial-like tissue developing outside the uterus due to an immune system dysfunction.
Factors that are at risk
Endometriosis is more likely to occur if you have one or more of the following factors:
The metamorphosis of embryonic cells. Embryonic cells, which are still in the early stages of development, can be transformed into endometrial-like cell implants by hormones like oestrogen throughout puberty.
Implantation of a surgical scar. Endometrial cells may cling to a surgical incision following a hysterectomy or C-section, for example.
Transport of endometrial cells: Endometrial cells may be transported to different areas of the body through blood arteries or tissue fluid (lymphatic) systems.
Affects the immune system The body may be unable to identify and remove endometrial-like tissue that has grown outside the uterus due to an immune system dysfunction.
Factors of danger
Endometriosis is caused by a number of reasons, including:
- Never having a child
- Starting your menstruation at a young age is a good idea.
- Experiencing menopause at a later age
- Menstrual cycles that are fewer than 27 days long, for example.
- Menstrual cycles that last more than seven days are considered heavy.
- Having higher oestrogen levels in your body or a longer lifetime exposure to oestrogen produced by your body
- BMI (body mass index) low
- Endometriosis in one or more relatives (mother, aunt, or sister)
- Any medical disease that stops blood from leaving the body during menstruation.
- Obstetrical and gynaecological problems
Endometriosis normally appears several years after menstruation begins (menarche). Unless you're using oestrogen, the signs and symptoms of endometriosis may improve momentarily during pregnancy and disappear entirely after menopause.
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor will ask you to explain your symptoms, including the location of your pain and when it happens, in order to identify endometriosis and other disorders that can cause pelvic discomfort.
The following tests can be used to look for physical signs of endometriosis:
Examining the pelvis. A pelvic exam involves your doctor manually palpating parts of your pelvis for abnormalities such as cysts on your reproductive organs or scars behind your uterus. Small regions of endometriosis are sometimes difficult to detect until they have caused a cyst to develop.
Ultrasound. This test creates pictures of the interior of your body using high-frequency sound waves. A transducer is either pushed against your abdomen or put into your vaginal canal to acquire the pictures (transvaginal ultrasound).
To gain the greatest image of the reproductive organs, both forms of ultrasonography might be used. Although a routine ultrasound imaging test won't tell your doctor if you have endometriosis, it can detect cysts linked with the disease (endometriomas).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging that (MRI). An MRI is a test that creates comprehensive pictures of your organs and tissues using a magnetic field and radio waves. An MRI can aid surgery planning by providing comprehensive information about the position and size of endometrial implants to your physician.
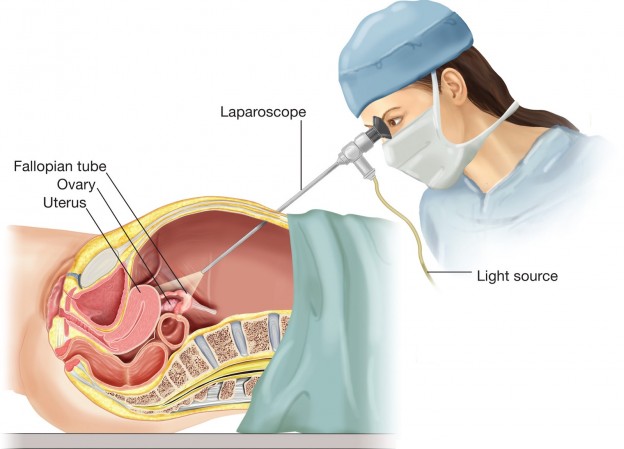
Laparoscopy. Your doctor may send you to a surgeon for an operation that permits the surgeon to see into your abdomen (laparoscopy).
Your surgeon creates a small incision around your navel and inserts a narrow viewing equipment (laparoscope) to examine for evidence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus while you're under general anaesthesia. The location, extent, and size of endometrial implants may all be determined using a laparoscopy. A tissue sample (biopsy) may be taken by your surgeon for further testing. Your surgeon may be able to totally treat endometriosis during the laparoscopy with correct surgical planning, resulting in only one procedure.
Disease Treatment:
Endometriosis is generally treated with medication or surgery. The route you and your doctor choose will be determined by the severity of your signs and symptoms, as well as whether or not you want to get pregnant.
Doctors often advise patients to attempt conservative therapy options first, with surgery as a last resort if the first treatment fails.
Pain relievers: To reduce uncomfortable menstrual cramps, your doctor may prescribe an over-the-counter pain medicine
If you're not attempting to conceive, your doctor may suggest hormone treatment in conjunction with pain medicines.
Hormone therapy : Endometriosis discomfort can be reduced or eliminated with the use of supplemental hormones. Endometrial implants thicken, break down, and bleed when hormone levels rise and decrease during the menstrual cycle. Hormone therapy may help to reduce endometrial tissue development and prevent new endometrial tissue implants. Hormone treatment isn't a long-term solution for endometriosis. After quitting therapy, you may notice a recurrence of your symptoms.
Endometriosis is treated using the following therapies:
Hormonal contraceptives are a type of hormonal contraception. Birth control pills, patches, and vaginal rings help regulate the hormones that cause endometrial tissue to develop up each month. When using a hormonal contraceptive, many women have lighter and shorter menstrual flow. In certain circumstances, using hormonal contraceptives — particularly continuous-cycle regimens — can help to minimise or eliminate discomfort.
Agonists and antagonists of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH). These medications stop ovarian-stimulating hormones from being produced, reducing oestrogen levels and preventing menstruation. Endometrial tissue shrinks as a result of this. Taking a modest dosage of oestrogen or progestin combined with Gn-RH agonists and antagonists may reduce menopausal adverse effects such hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and bone loss since these medicines promote artificial menopause. When you stop using the medicine, your menstrual cycles and ability to become pregnant return.
Progestin treatment is a type of hormone replacement therapy. A variety of progestin therapies, such as an intrauterine device containing levonorgestrel (Mirena, Skyla), a contraceptive implant (Nexplanon), a contraceptive injection (Depo-Provera), or a progestin pill (Camila), can stop menstrual periods and endometrial implant growth, potentially alleviating endometriosis signs and symptoms.
Inhibitors of the aromatase enzyme. Aromatase inhibitors are a type of drug that lowers oestrogen levels in the body. To treat endometriosis, your doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor in conjunction with a progestin or a combined hormonal contraceptive.
Minimal invasive Surgery.
If you have endometriosis and are attempting to conceive, conservative surgery (removal of endometriosis implants while keeping the uterus and ovaries) may improve your chances. Surgery may be beneficial if you have severe endometriosis discomfort; nevertheless, endometriosis and pain may recur.
In more extreme situations, your doctor may do this treatment laparoscopically or, less usually, through standard abdominal surgery. The majority of instances of endometriosis may be treated by laparoscopic surgery, even in severe situations.
Your surgeon will introduce a slender viewing instrument (laparoscope) via a tiny incision near your navel and instruments to remove endometrial tissue through another small incision during laparoscopic surgery. Following surgery, your doctor may advise you to take hormone medicine to aid with pain management.
Treatment for infertility
Endometriosis can make it difficult to conceive. If you're having trouble conceiving, your doctor may suggest fertility medication under the supervision of a reproductive expert. Treatments for infertility range from stimulating your ovaries to in vitro conception. Your specific scenario will determine which treatment is best for you.
The ovaries are removed during a hysterectomy.
Endometriosis was originally thought to be best treated by surgery to remove the uterus (hysterectomy) and ovaries (oophorectomy). Endometriosis specialists, on the other hand, are shifting away from this method and focusing instead on the cautious and comprehensive excision of all endometriosis tissue.
Menopause occurs when your ovaries are eliminated. For some, the absence of hormones released by the ovaries may alleviate endometriosis discomfort, while for others, endometriosis that persists after surgery causes problems. Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) illnesses, certain metabolic problems, and early mortality are among risks associated with early menopause.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
1 Days
Days in Hotel
*
3 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Sudhir Sharma
Bariatric Surgeon- Laparoscopic surgeon, Kidney Stone Specialist, Gastric Sleeve Surgery, Piles Treatment (Non Surgical), Removal Of Stitches Procedure, Gastric Bypass Surgery, Gastric Band Surgery, Gastric Balloon Treatment, Fitsula treatment
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
21 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Sanjay Verma
General surgeon- Laparoscopic surgeon
Fortis Escorts Heart Institute New Delhi, India
20 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Anand Kumar Chaturvedi
General surgeon- Hernia Surgeon, Appendicectomy, General Surgery, Laparoscopic Appendicectomy, Fitsula treatment, General Surgery, General Surgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
45 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Kavita Saxena
General surgeon- Laparoscopic surgeon, Hernia Surgeon, Hernia Surgeon, Hernia Surgeon, Piles Surgeon, Cryotherapy, Breast surgery & MIPH (For Hemorrhoids and Ano reetal surgeries)
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
35 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Shilpa Verma
Lapasoscopic Surgeon- Laparoscopic Surgery, Laparoscopic Surgery, Rhinoplasty, Abdominoplasty, Abdominoplasty, Rhinoplasty, Piles Surgery, Piles Treatment (Non Surgical), Piles Treatment (Non Surgical), Laparoscopic Surgery, Abdominoplasty, Face Lift/ Rhytidectomy, Rhinoplasty, Piles Surgery, Laparoscopic Surgery, Piles Surgery, Piles Treatment (Non Surgical), Abdominoplasty, Face Lift/ Rhytidectomy, Rhinoplasty, Laparoscopic Surgery, Laparoscopic Surgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
21 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Anil Sharma
General surgeon- Hepatobiliary, Hepatobiliary, Gall Bladder Surgeon, Appendix Surgeon, Scarless neck surgery, Bariatric & Metabolic Surgery, Fistula Surgery, Piles Surgery, Diabetes Mellitus, Bariatric & Metabolic Surgery, Weight loss metabolic surgery, Scarless surgery, Cardiomyotomy, Obesity Surgery, Piles Surgery, Fissure, Fistula Surgery, Laproscopic Fundoplication, laparoscopic abdominal and inguinal hernia repair, Treatment of Hernia, Piles Surgery, Thyroid and parotid surgeries
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr P K Dewan
Bariatric Surgeon- Gastrointestinal surgery, Laparoscopic surgeon, Gallbladder Surgeon, Fistula Surgeon, Fistula Surgeon, Hernia Repair Surgery, Anal Fissure Surgery, Anal Fissure Treatment (Non-Surgical), Diabetic Foot, Endoscopic Surgery, Hemorrhoids, Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic, Incisional Hernia, Laparoscopic Abdominal Surgery, Navel Laparoscopic, Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic, Hemorrhoids, Endoscopic Surgery
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
42 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ajay Jain
General surgeon- Cardiothoracic anesthesiology, Bariatric Surgeon, Hernia Surgeon, Cancer Surgeon, Laparoscopic surgeon, Hernia Surgeon, Liver Transplant, Hernia Surgeon, Laparoscopic surgeon, Bariatric Surgeon, Kidney Transplant, Breast Surgery, GI Surgery, Minimal Access Surgery, Piles Surgery, Thoracic Surgery, General Surgery, Breast Surgery, Piles Surgery, Kidney Transplant, Liver Transplant, Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy, Kidney Transplant, General Surgery, Piles Surgery, Advanced Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgeries, GI Surgery, Minimal Access Surgery, General Surgery, Lung Tranplantation, GI Surgery, Breast Surgery
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Bachan Singh Barthwal
General surgeon- Gall Bladder Surgeon, Minimally invasive surgery, Gastric Band Surgery, Minor Surgery, Laparoscopic hernia surgery (All types), Minor Surgery, Laparoscopic Appendicectomy, Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy, Laparoscopy for Hiatus Hernia, Fitsula treatment
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
34 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Ashok Sabharwal
General surgeon- Hiatus Hernia Surgery, Laparoscopic hernia surgery (All types), Laparoscopic Appendicectomy, Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy, Laproscopic Spleenectomy, Laproscopic Fundoplication, Minimally Invasive Procedure for PILES or Stapler, Video Assisted Anal Fistula Treatment, Laparoscopic Bile duct, Stones Surgery, Laparoscopy for Achalasia Cardia, Laparoscopy for Hiatus Hernia, Laparoscopy for Pseudopancreatic Cysts, Laparoscopy in various Liver Cysts
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
27 Years of Experience