AVSD Closure
India
-
Our Price USD 5850
-
Hospital Price USD 6500
-
You Save : USD 650
Booking Amount: USD 585. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
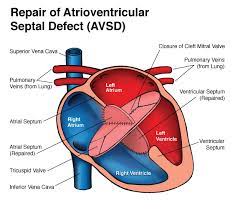
AVSD Closure:
The cornerstone of treatment for children with AVSD is open-heart surgery. The repair entails dividing the common valve into right and left sides and closing the holes with one or two patches. This is done after the heart/lung bypass procedure to keep the circulation going while the repair is being done. To reduce valve leakage, stitches are also inserted in the valve. The surgical repair results are excellent, with 95 percent of patients surviving without severe problems. Abnormal cardiac rhythm and persistent valve leakage are two complications.
Disease Overview
Pulmonary vascular disease
PVD (pulmonary vascular disease) is a general word that refers to any disorder that affects the lungs' blood vessels. These veins transport oxygen-depleted blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary arteries transport deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where oxygen is taken up.
Disease Signs and Symptoms
Several variables influence the symptoms of pulmonary vascular disease:
The rapidity with which the procedure affecting the pulmonary blood vessels occurred
Which blood vessels in the lungs are affected? (where the pulmonary vascular disease is)
What portion of the pulmonary vascular system is impacted?
A rapid, significant pulmonary embolism, for example, might cause severe shortness of breath and chest discomfort by obstructing a big pulmonary artery. However, a little pulmonary embolism (one that affects only a tiny blood artery) may go unnoticed.
Although the symptoms of pulmonary vascular disease vary, each of the sources of the disease has a set of common symptoms:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a condition that causes shortness of breath that worsens over time. Chest discomfort or fainting (syncope) with effort might develop as the disease progresses.
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that forms abruptly in the lungs. Shortness of breath, chest discomfort (which is exacerbated by deep breathing), and a fast heart rate are all typical symptoms. Depending on the size of the blood clot, pulmonary embolism symptoms can range from mild to severe (s).
Pulmonary venous hypertension: This kind of pulmonary vascular illness is associated with shortness of breath due to the presence of congestive heart failure. Shortness of breath can be exacerbated by resting flat, having an unstable blood pressure, or having too much fluid in the body (edema).
Disease Causes:
The causes of pulmonary vascular disease differ depending on which blood arteries in the lungs are afflicted. There are various types of pulmonary vascular disease:
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is a condition in which the blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries is elevated (carrying blood away from the heart to the lungs). Lung illness, autoimmune disease, or heart failure can all contribute to pulmonary arterial hypertension. Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension occurs when there is no obvious reason.
Pulmonary Venous Hypertension (PVH) is characterized by an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary veins (carrying blood away from the lungs, to the heart). Congestive heart failure is the most common cause of pulmonary venous hypertension. Pseudo-venous hypertension can be caused by a defective mitral valve in the heart (mitral stenosis or regurgitation).
A blood clot breaks off from a deep vein (typically in the leg), travels to the right heart, and is pumped into the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Occasionally, rather than a blood clot, an embolism might be a huge bubble of air or a ball of fat.
Disease Diagnosis:
A clinician may suspect the presence of pulmonary vascular disease based on a patient's symptoms, indicators, and medical history. One or more of the following tests are commonly used to diagnose pulmonary vascular disease:
CT scan: A CT scanner collects several X-rays and uses a computer to create detailed pictures of the lungs and chest. A pulmonary embolism in a pulmonary artery may generally be detected with CT scanning. CT scans might also reveal issues with the lungs itself.
The V/Q scan (ventilation/perfusion scan) is a nuclear medicine diagnostic that takes pictures of how effectively the lungs fill with air. Photographs of blood flow via the pulmonary blood arteries are compared to those of those images. Unmatched regions might indicate the presence of a pulmonary embolism (blood clot).
An ultrasound video of the beating heart is called an echocardiography. An echocardiography can detect congestive heart failure, heart valve disease, and other disorders that contribute to pulmonary vascular disease.
A pressure sensor is put into a vein in the neck or groyne during right cardiac catheterization. The sensor is advanced via the veins, into the right heart, and finally into the pulmonary artery by a doctor. The best way to identify pulmonary arterial hypertension is to have a right cardiac catheterization.
X-ray film of the chest: Pulmonary vascular disease cannot be diagnosed with a simple chest X-ray. However, it may reveal underlying lung illness or enlargements in the pulmonary arteries, which might indicate pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Angiography (angiography) of the pulmonary arterial system: Contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream, and X-ray scans of the chest provide detailed views of the pulmonary artery system. Angiography is quite effective in diagnosing pulmonary embolism, however it is no longer used because CT scans are more convenient, less invasive, and have a reduced risk.
Disease Treatment:
Pulmonary vascular disease can be treated in a variety of ways. The aetiology of pulmonary vascular disease determines how it is treated.
Blood thinners are used to treat pulmonary embolisms (blood clots in the lungs) (anticoagulation).
Chronic thromboembolic illness: In severe cases of thromboembolic disease, surgery to clear the pulmonary arteries may be required (thromboendarterectomy). In addition, blood thinners are utilised.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) can be treated using a variety of medications that reduce blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension has been demonstrated to benefit the most from these medicines.
If another condition causes pulmonary vascular disease, addressing that condition may help to improve the pulmonary vascular disease:
Drugs that inhibit the immune system are commonly used to treat autoimmune illnesses such as lupus, scleroderma, and Sjogren's syndrome.
In patients with pulmonary vascular disease who have low blood oxygen levels (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease), breathed oxygen can help halt the course of the condition.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
10 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Gaurav Kumar
Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon- Arterial switch operation, Double switch operation, Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, Arch repair, ASD VSD repair, Tetralogy of Fallot repair, Truncus arteriosus repair, Rastelli operation & Cone repair and cardiac transplant
Narayana Super Speciality hospitals Gurgaon, India
21 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Mahkar Singh Khari
Cardiologist- Preventive cardiology and Cardiac Rehabilitation, Ultrasound, Peripheral Angiography, PDA, Holter Monitoring, Hypertriglyceridemia, Pulmonary Function Test (PFT), ECG analysis, Hypercholesterolemia, Hypertriglyceridemia, Device closure of ASD/VSD/PDA, Holter Monitoring
Yatharth Super Speciality Hospital Noida, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Bipin Kumar Dubey
Cardiologist- Angioplasty, ICD implantation, Coronary interventions, Balloon aortic valvotomy, Balloon pulmonary valvotomy, Paediatric cardiology, Baloon mitral valvotomy, Angioplasty, Balloon Mitral Valbuloplasty
Manipal Hospitals New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Krishna yadav
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatrics, General Surgery, General Surgery, General Surgery
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
56 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Brahmadeva Dwivedi
Pediatric surgeon- Bariatric Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Vascular Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Bariatric Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Vascular Surgeon, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgeon, General Surgery, General Surgery, General Surgery, Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgery, Pediatric Kidney Diseases, Pediatric Cancer Surgery, Pediatric Liver Transplant, Pediatric Lung Transplant, Pediatric Gastric Internal Surgery
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
63 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Meera Luthra
Pediatric surgeon- Laparoscopic and Miniamally Invasive Surgery, Newborn and Thoracoscopy
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
38 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rakesh Handa
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgeon, Neonatal Surgeon, Hypospadias Surgery, Surgery for Spinal Dysraphism
MAX Super Speciality hospital, Patpadganj Delhi New Delhi, India
38 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Anurag Krishna
Pediatric surgeon- Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Pediatric Laparoscopic Surgeon, Neonatal Surgeon, Endourology, Kidney obstructions, VU reflux, Complex birth defects, Hypospadias Surgery, Endourology
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
35 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Nasir Munim
Pediatrician- Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, Allergy Testing, Infant & Child nutrition, Allergy Testing, Atrial Septal Defects (ASDS), Thyroid disorder, Vaccination/ Immunization, Chickenpox Treatment, Asthma, Jaundice Treatment, Asthma, Cerebral Palsy, Vaccination/ Immunization, Infant & Child nutrition, Chickenpox Treatment, Chickenpox Treatment, Allergy Testing, Infant & Child nutrition, Bedwetting treatment and management, Polio, Infant & Child nutrition, Child Care, Lactation problems, Management of Restless Child Disorder, Child and Adolescent Problems, Chickenpox Treatment, Cerebral Palsy, Neurofibromatosis, Treatment of Sids, Cough in Children, Management of Growth Retardation, Multiple System Atrophy, Jaundice Treatment, Child and Adolescent Problems, Asthma, Allergy Testing
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
20 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Anil Bhan
Cardiac Surgeon- Pediatric Cardiology, Pediatric Cardiac Surgeon
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
37 Years of Experience